Ons aanbod
Uw project,
onze zorg
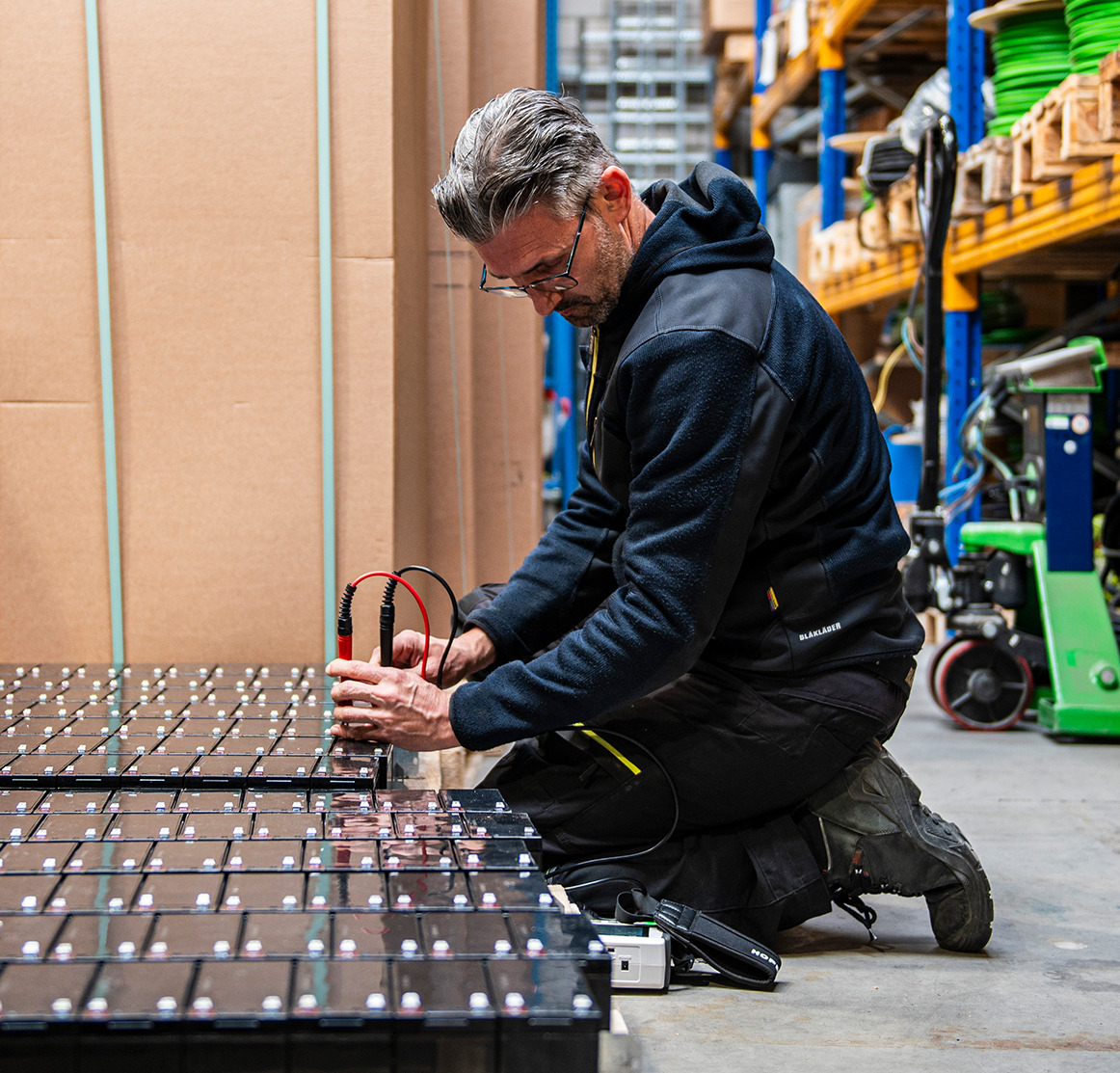
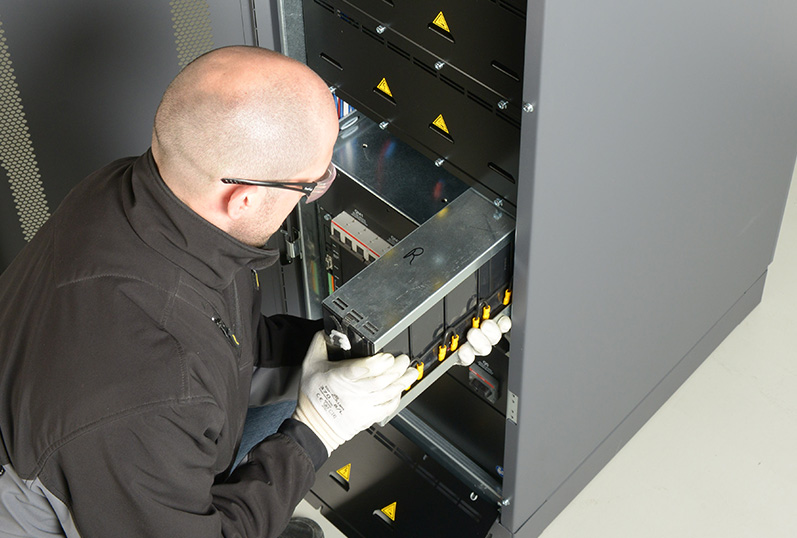
Wij voeren alle UPS noodreparaties uit met onze getrainde UPS monteurs, u hebt geen contract nodig, neem contact op, wij praten graag.
In een noodsituatie waarin u geen stroom meer hebt, door een stroomstoring als gevolg van het weer, een mechanisch defect of slijtage van onderdelen door veranderingen in de bedrijfsomgeving, kunt u rekenen op PK Solutions om u in een mum van tijd weer aan de gang te krijgen.
Onze
kwaliteiten

Klantgericht

Gepassioneerd

25 jaar ervaring

Innovatief